
It provides a snapshot of the firm’s net worth over a period, smoothing out fluctuations and giving a more stable perspective on its financial standing. By using the above calculation, one can calculate the total asset of a company at any point in time. So, for example, if A has a 20 percent contribution and B has a 40 percent contribution, the latter’s share would be more than the former when the company liquidates or makes significant profits. Total the current and long-term liabilities subtotals to get the total liabilities. Understand how a company’s financial results connect to its ownership structure. Many public companies also provide their financial statements directly on their investor relations sections of their official websites.
What does the balance sheet formula represent?
- The value can be both positive and negative, depending on the number of assets the companies own and their liabilities.
- Retained Earnings indicates the profits accumulated over time and not distributed to shareholders.
- Additional Paid-in Capital, sometimes called Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par, records the amount investors pay for stock above its par value.
- These private equity investors can include institutions like pension funds, university endowments, insurance companies, or accredited individuals.
- At the end of its fiscal year 2024, Apple had an accumulated deficit of $19.2 billion.
- Unlike public corporations, private companies do not need to report financials or disclose financial statements.
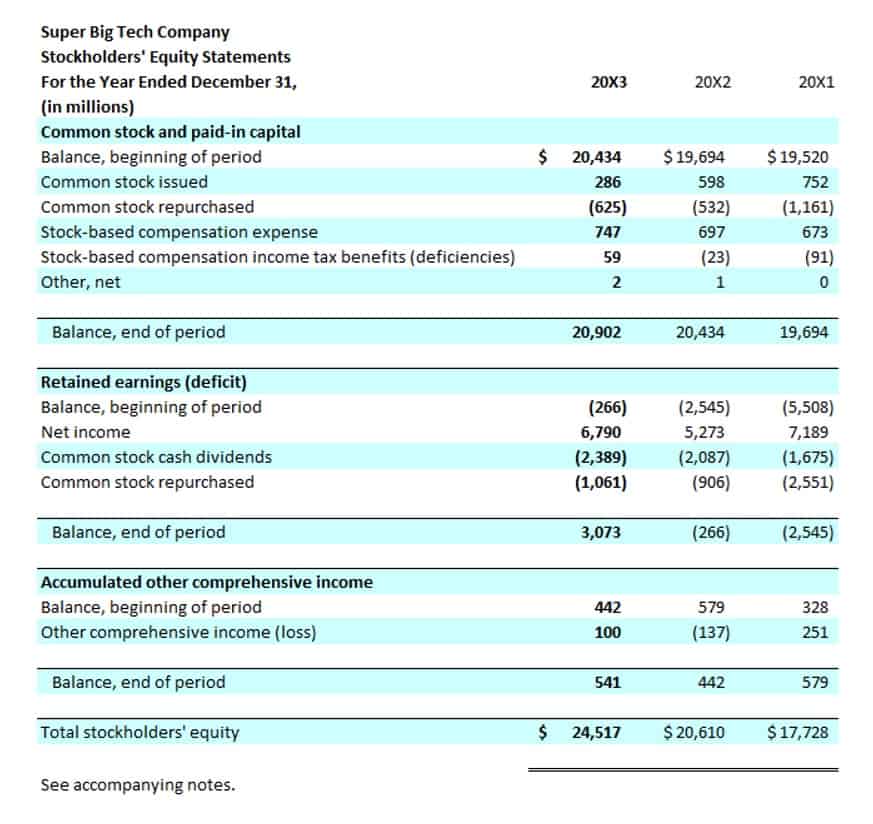
Preferred stockholders receive fixed dividends before common stockholders and have priority in receiving payments if the company liquidates, though they often do not have voting rights. Amounts received for preferred stock above its par value are recorded as additional paid-in capital. Stockholders’ equity represents the owners’ claim on a company’s assets after all liabilities have been settled.
Look at the balance sheet’s stockholders’ equity section
Thus, a shareholder concerned for his earnings will also be concerned for the company. An alternative calculation of company equity is the value of share capital and retained earnings less the value of treasury shares. Subtracting liabilities from assets, we see that shareholders’ equity was therefore $66.8 billion ($331.2 billion -$264.4 billion). This is the same figure reported lower on the balance sheet, under shareholder equity. The stockholders’ equity number provides a snapshot of a company’s net worth.
Utilizing for Investment Decisions

This total matches the company’s assets, ensuring the balance sheet is balanced. Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (AOCI) includes certain gains and losses that bypass the income statement and are instead reported directly in equity. While complex, its inclusion ensures that all changes in equity, other than those from owner investments and dividends, are accounted for. An asset is what a company owns and from which the liabilities are subtracted to obtain its equity value. In short, the asset value can be calculated by adding the firm’s equity and total debt or liabilities.

Profits increase stockholders’ equity, so when working backward, we must subtract them to move from ending to beginning stockholders’ equity. For example, a company’s brand name could be considered an asset, but it’s tough to say exactly what that brand name is worth. The market value of real estate and equipment is also somewhat of an estimate. After all, the only way to know exactly what a building is worth is to sell it. Master combining core financial elements to understand a company’s funding structure and financial health.
- The balance sheet, often referred to as the statement of financial position, provides a snapshot of a company’s assets, liabilities, and equity at a specific point in time.
- From the beginning balance, we’ll add the net income of $40,000 for the current period, and then subtract the $2,500 in dividends distributed to common shareholders.
- Although many investment decisions depend on the level of risk we want to undertake, we cannot neglect all the key components covered above.
- The shareholders’ equity number is a company’s total assets minus its total liabilities.
- The liabilities to be aggregated for the calculation are accounts payable, accrued liabilities, short-term debt, unearned revenue, long-term debt, and other liabilities.
For example, if a company reports total assets of $500,000 and total liabilities of $200,000, its shareholders’ equity would be calculated as $500,000 minus $200,000, resulting in $300,000. This method quickly reveals the residual claim of the owners on the company’s resources. It emphasizes how to find total stockholders equity the foundational relationship between a company’s resources and how those resources are funded, whether by creditors or by the owners themselves. Imagine this company’s balance sheet reports its total liabilities as $750,000.

Conversely, a lower ratio implies higher reliance on debt financing, which can increase financial risk. InvestingPro offers detailed insights into companies’ Degree of Financial Leverage including sector benchmarks and competitor analysis. She holds a Bachelor of Science in Finance degree from Bridgewater State University and helps develop Outsource Invoicing content strategies. Shareholders consider this to be an important metric because the higher the equity, the more stable and healthy the company is likely to be.
- Long-term liabilities are those that are due for repayment in periods beyond one year; they include bonds payable, leases, and pension obligations.
- These elements shape the understanding of a company’s equity position and provide insights into shareholder value.
- Shareholders’ equity provides crucial insights into a company’s fiscal health and the value returned to shareholders.
- Please remember, when calculating stockholders’ equity in a real-world situation, always ensure the accounting equation is balanced.
- Shareholders’ equity represents the amount of assets remaining if a company paid off all its liabilities.
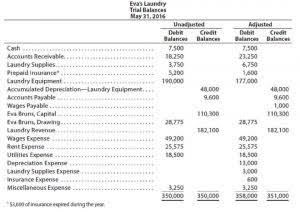
If these specific totals are not explicitly listed, you may need to sum the individual liability accounts and individual equity accounts to arrive at their respective totals. Equity is the remaining value of an asset or investment after considering or paying any debt owed; the term is also used to refer to capital used for funding or a brand’s value. So from the above-given information, we will calculate the total equity using the equations mentioned above.
When the balance sheet is not available, the shareholder’s equity can be calculated by summarizing the total amount of all assets and subtracting the total amount of all liabilities. By comparing total equity to total assets belonging to a company, the shareholders equity ratio is thus a measure of the proportion of a company’s asset base financed via equity. Let us consider another example of a company SDF Ltd to compute the stockholder’s equity. As per the company’s balance sheet for the financial year ended https://duta169.com/invoice-help-invoice-vs-order-details/ on March 31, 20XX, the company’s total assets and total liabilities stood at $3,000,000 and $2,200,000, respectively. Based on the information, determine the stockholder’s equity of the company.
